All developers can relate to this- a late-night deployment, a minor change, and suddenly a critical feature is broken. Hours slip away as you scramble to fix something that worked yesterday. What if you could prevent that panic before it even starts?
Every Laravel developer knows the relief of seeing an application run smoothly after an update. But how do you guarantee it keeps working tomorrow, next week, or six months from now? The answer is Laravel automated testing.
By building tests directly into your Laravel projects, you can catch problems early, maintain confidence in your code, and free yourself from repetitive manual testing. Automated tests don’t just save time; they help your team move faster, ship features with fewer surprises, and ensure that quality doesn’t slip as your application grows.
This guide breaks down why test automation is essential in Laravel, the exact Laravel testing tools you need, and the strategies that make automation sustainable. By the end, you’ll have a clear roadmap for building a robust, automated testing pipeline in Laravel that catches bugs early and lets you ship with confidence.
Why Should You Automate Tests on Laravel?
Whether you are working with your in-house team or planning to hire expert Laravel developer, you’ll find that Laravel applications often grow quickly, with new features, API integrations, and user interactions layered on top of one another. Manual testing might work at the start, but it quickly becomes unsustainable as the application expands.
When you automate your tests, you:
- Save time on repetitive checks: Instead of manually clicking through forms or running the same commands, your tests verify functionality in seconds.
- Catch regressions early: For example, changing a global scope on a model could unexpectedly alter a dozen different API responses. Laravel automated testing will catch this instantly.
- Support continuous delivery: With reliable tests, you can enhance Laravel CI/CD workflow, release updates more frequently without fearing that hidden bugs will slip through.
- Improve collaboration: A test named it_calculates_the_correct_order_total_with_tax() serves as clearer documentation than a complex method in a service class.
- Protect long-term stability: As your Laravel project scales, automated testing keeps technical debt and fragile code under control.
For developers working with Laravel, automating tests isn’t optional; it’s the foundation of a maintainable, scalable, and resilient application.
A. Laravel Testing Tools Overview
Laravel gives you a rich set of tools to cover every layer of your application, but knowing which to use and when, makes all the difference. Here’s a quick overview of all the tools you’ll get as part of the Laravel testing process.
PHPUnit vs Pest: Which Should You Use in Laravel?
PHPUnit is the default testing framework in Laravel and a reliable choice for unit and feature tests. It ensures that your application’s core logic works exactly as intended. Pest builds on top of PHPUnit but offers an elegant, fluent syntax and a focus on the expectations API, making tests easier to write and understand. While there’s an ongoing debate on PHPUnit vs Pest Laravel, both are excellent for validating business rules, models, and controllers.
For True Unit Testing: Mockery
Laravel integrates smoothly with Mockery, a powerful mocking library. It allows you to isolate classes from their dependencies, making it possible to test individual service or action classes without relying on a full database or framework setup.
For API and Application Endpoints: Laravel’s HTTP Test Helpers
Before reaching for a full browser, Laravel’s built-in testing helpers let you make HTTP requests to your application, inspect responses, and assert JSON structures. This is the fastest and most efficient way to test controllers and API routes without spinning up a browser.
For User Interactions: Laravel Dusk
When you need to simulate how real users interact with your application in the browser, Dusk is the tool to reach for. It uses the real Chrome browser via ChromeDriver to interact with your frontend exactly as a user would, verifying clicks, forms, navigation, and JavaScript behaviors in a realistic environment.
For Code Quality: PHPStan and PHPCS
PHPStan and PHPCS for Laravel code quality are static analysis tools, meaning they analyze your code without executing it. PHPStan detects potential type and logic errors early, while PHP CodeSniffer (PHPCS) enforces coding standards. Together, they keep your codebase clean, consistent, and less prone to hidden issues.
For CI/CD: GitHub Actions
Laravel GitHub Actions isn’t a testing tool itself; rather, it’s a CI/CD orchestrator that runs your tests. It ensures the same checks you run locally are consistently applied across the team whenever someone pushes code to the repository.
With this toolkit, you can cover everything from low-level logic to full browser interactions, while ensuring that the code itself remains reliable and maintainable.
B. The Core Strategies for Test Automation
Having the right tools is only half the battle. To get real value from test automation in Laravel, and optimize Laravel performance, you need strategies that make your tests reliable, efficient, and scalable.
What Is the Laravel Testing Pyramid?
The testing pyramid emphasizes writing more unit tests than integration or end-to-end tests. In Laravel, that looks like this:
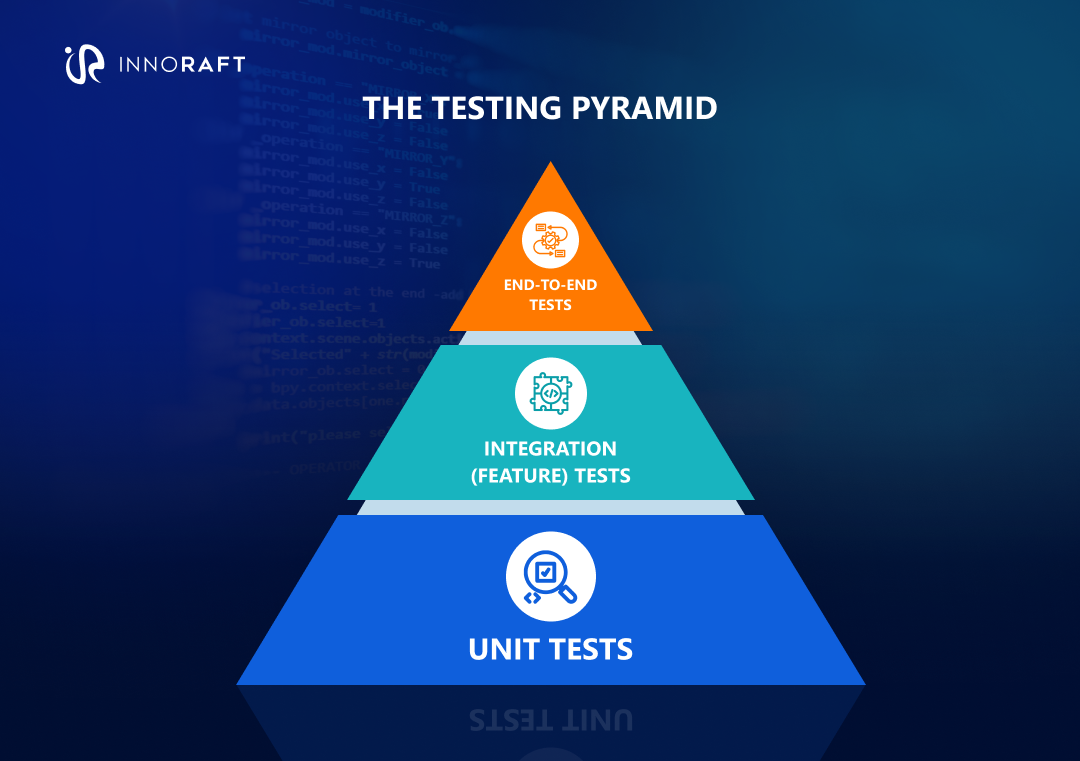
- Unit tests: Perfect for testing individual Action or Service classes in isolation using mocks.
- Integration (Feature) tests: Laravel’s sweet spot. Use HTTP tests to verify that a request to a controller route correctly interacts with models and returns the expected response.
- End-to-end tests: Use Dusk for critical user journeys, like the full user registration and onboarding flow.
This balance keeps your test suite fast while still ensuring confidence at every level.
How Does TDD Work in Laravel?
Test-driven development in Laravel flips the usual workflow. You write a test before the code, then build just enough logic to make it pass.
Imagine the workflow for a new API endpoint:
- Red: Write a test:
$this->postJson('/api/posts', $data)->assertStatus(201);Run it. It fails because the route doesn’t exist.
2. Green: Create the route and a minimal controller method to return a 201. The test now passes.
3. Refactor: Add validation, save the model, and improve the code, ensuring the test stays green.
TDD in Laravel helps you design cleaner controllers, more reusable services, and fewer hidden dependencies.
How to Keep Laravel Tests Isolated and Reliable?
Reliable tests don’t leak into each other. Laravel helps with the RefreshDatabase trait, which resets your data between tests. The RefreshDatabase trait resets your database, but database factories are what make test isolation practical and powerful..
For example:
User::factory()->create(['is_admin' => true]);Factories generate predictable test data for each test, ensuring one test never relies on the state of another.
Why Automate The Safety Net with CI/CD?
Manual test execution only goes so far. By embedding your tests into a Laravel CI/CD workflow, every change triggers automated checks. Tools like GitHub Actions or GitLab CI make this simple to set up. This approach ensures that the safety net is always in place, guarding against regressions before they ever reach production.
C. A Simple Laravel Testing Workflow You Can Follow
Laravel automated testing can feel overwhelming at first, but in practice, setting up a smooth testing workflow in Laravel follows a logical sequence.
Here’s a straightforward workflow you can adopt:
Write unit and feature tests with PHPUnit or Pest
Use artisan commands to get started (e.g., php artisan make:test UserRegistrationTest). Start by covering your application's core logic—models, services, and controller actions.
Add end-to-end tests with Laravel Dusk browser testing
Extend coverage to browser flows (e.g., php artisan dusk:make LoginTest). Validate user logins, form submissions, and checkout processes.
Use PHPStan and PHPCS for Laravel code quality
Run static analysis and style checks locally with a pre-commit hook or inside your CI pipeline. This catches potential bugs and style issues before they're ever merged.
Automate execution with Laravel GitHub Actions
Create a simple YAML file in .github/workflows that installs dependencies, sets up your .env file, and runs php artisan test.
Integrate into CI/CD for deployments
Configure your deployment tool (e.g., Laravel Forge or Ploi) to only trigger deployments if the GitHub Actions workflow succeeds.
This workflow scales well whether you’re a solo developer or part of a larger team. Over time, it becomes a natural part of development rather than an afterthought.
Conclusion
Test automation in Laravel isn’t just a technical best practice, it’s a long-term investment in stability, speed, and confidence. By combining the right tools with proven strategies, you build a development process that supports growth instead of slowing it down.
Key takeaways:
- Laravel’s HTTP testing helpers make feature testing fast and efficient.
- HPUnit and Pest cover core logic with a focus on clarity and reliability.
- Laravel Dusk browser testing simulates real user flows with a full browser.
- GitHub Actions ensures your tests run consistently in CI/CD pipelines.
- PHPStan and PHPCS provide static analysis for higher code quality.
- Mockery enables isolated unit testing of service and action classes.
- Strategies like the testing pyramid, TDD, factories for isolation, and CI/CD automation make your tests faster, more reliable, and more effective.
- A simple, actionable workflow ties these practices together.
With these practices you can ensure that testing becomes your application’s strongest asset, giving you the freedom to build, innovate, and refactor without fear.
Want to know more about how to automate testing in Laravel? Connect with our experts.
FAQ
Frequently Asked Questions
Didn’t find what you were looking for here?